![]() Introduction
to Protein Structure
Introduction
to Protein Structure
Acid / Base Chemistry of Amino Acids
Both the amino group and the carboxyl group of each amino acid are ionizable. The carboxyl group (with a pKa of about 3) is deprotonated at physiological pH. The amino group is protonated at physiological pH. (The pKa of ammonium ions is about 9.)
Thus, amino acids exist at zwitterions ("twin ions") at physiological pH:
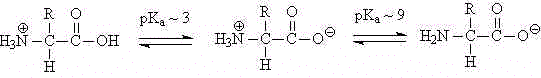
In addition, the side chains of some of the amino acids contain ionizable groups.
| Amino Acid | pKa | Functional Group |
Acid/Base Chemistry |
| Aspartate & Glutamate | 4.4 | carboxyl |
|
| Histidine | 6.5 | imidazole | 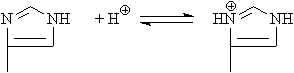 |
| Cysteine | 8.5 | sulfhydryl | |
| Lysine | 10.0 | amine | |
| Tyrosine | 10.0 | phenol | 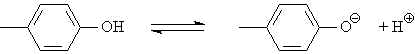 |
| Arginine | 12.0 | guanidinium | 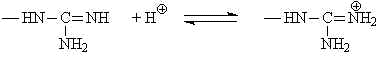 |
Examine the titration behavior of the amino acids in detail by going to this site at the University of Virginia.
Copyright © 1998, 1999, 2007 by Frank R. Gorga; Page maintained by F.R. Gorga; Last updated: 12-Mar-2007